While writing the previous article I recalled all the problems I had trying to decode the Motorola (formerly Symbol) WISP, WISPe, CAPWAP protcool used between the Wireless LAN Switch and their Access Ports.
As of WireShark version 0.99.7 there is decode support for the Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) protocol used by Airspace (Cisco) and a few other wireless vendors.
The legacy Motorola Wireless LAN WS5000, WS5100 switches (version 1.x and 2.x) utilize the WIreless Switch Protocol (WISP) while the Motorola Wireless LAN WS5100, RFS7000 (version 3.x and 1.x respectively) utilize the WIreless Switch Protocol Enhanced (WISPe). The WISPe protocol from Motorola very closely mimics the Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) that is currently being developed by the IETF.
Now that I’ve got that history lesson out of the way. Have you every needed to decode the protocol running between the Wireless Switch and the Access Ports?
As you know by now I have a large number of Motorola Wireless LAN switches and Access Ports deployed throughout my organization. Unfortunatley the latest version of WireShark does not support the decoding of WISP, WISPe, or CAPWAP.
Thankfully Ethereal v0.10.14 has decoders for the WISP and CAPWAP protocols. I will say this warning though. I have downloaded multiple copies of Ethereal v0.10.14 and some seem to support WISP and CAPWAP while others don’t appear to support it. If I find a link for a working version I’ll update this article.
Here’s an example of the WISP protocol between a Motorola Wireless LAN Switch (WS5000 v2.x) and an Access Port 300 (AP300). (click on the image to enlarge it)
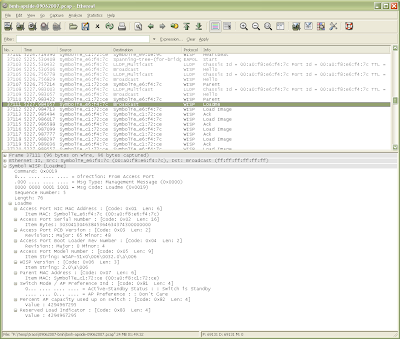 In the above trace you can see that the AP300 has just been reset and is in the process of booting. It starts by issuing EAPOL and LLDP packets before sending it’s first WISP “Hello”. You can see that the WS5000 responds to the “Hello” with a “Parent” command after which the Ap300 starts to download its runtime software with the “LoadMe” command.
In the above trace you can see that the AP300 has just been reset and is in the process of booting. It starts by issuing EAPOL and LLDP packets before sending it’s first WISP “Hello”. You can see that the WS5000 responds to the “Hello” with a “Parent” command after which the Ap300 starts to download its runtime software with the “LoadMe” command.
Here’s an example of the CAPWAP protocol between a Motorola Wireless LAN Switch (WS5100 v3.x) and an Access Port 300 (AP300). (click on the image to enlarge it)
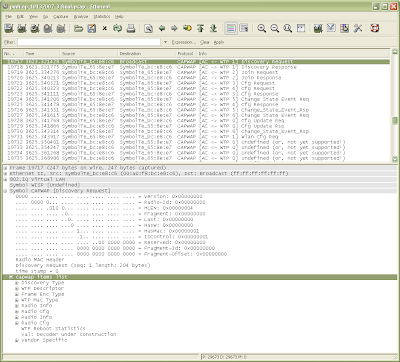 Note: this trace was not performed at the port level so we don’t see the EAPOL or LLDP traffic. We can see the AP300 making “Discovery”, “Join” and “Cfg” requests of the WS5100 switch.
Note: this trace was not performed at the port level so we don’t see the EAPOL or LLDP traffic. We can see the AP300 making “Discovery”, “Join” and “Cfg” requests of the WS5100 switch.
Cheers!
UPDATE: March 29, 2008
Here’s a link for Ethereal v0.10.14 that I believe should decode both WISP and CAPWAP;
http://www.michaelfmcnamara.com/files/wisp-ethereal-setup-0.10.14.exe