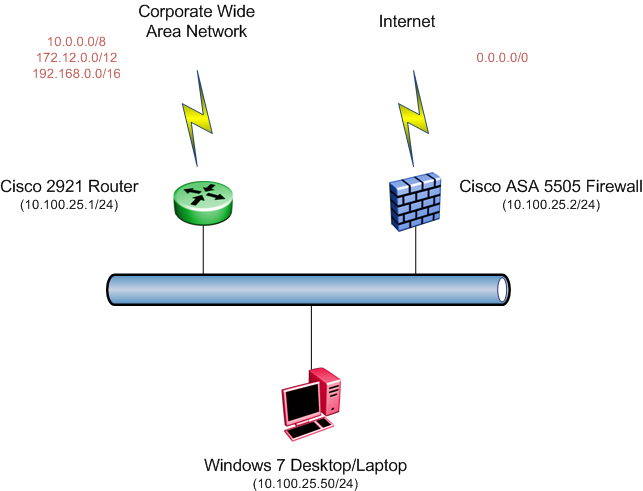
I’ve seen quite a few issues throughout the years but one that I run into time and time again revolves around which device to set as the default gateway, in a DHCP scope, when you have both an internal router and Internet firewall on the same IP network. Should you set the router as the default gateway or should you set the firewall as the default gateway? Let’s use the topology below as a pretty simple example;
Theoretically this shouldn’t be an issue but I’ve seen it be an issue time and time again. This configuration usually results in performance issues because ICMP redirects are ignored, or never issued.
Cisco 2921 Router – Default Gateway
If we set the default gateway for the Windows 7 desktop/laptop to the Cisco 2921 Router then all traffic that’s not local to this network will be sent to that router. That includes traffic for other corporate networks and for Internet traffic. In theory the Cisco 2921 Router will forward traffic destined for corporate networks out over the WAN while it will forward traffic for Internet based destinations to the Cisco ASA 5505 firewall. When it forwards traffic to the Internet it will also issue an ICMP redirect to the Windows 7 Desktop/Laptop informing that device that 10.100.25.2 is a better destination for traffic to the Internet.
Cisco ASA 5505 – Default Gateway
If we set the default gateway for the desktop/laptop to the Cisco ASA 5505 firewall then all traffic that’s not destined for the Internet will still be sent toward the firewall. In the case of the Cisco ASA 5505, since it’s a firewall it won’t issue ICMP redirects to the desktop/laptop so all traffic will need to pass through the Cisco ASA 5505.
What’s the solution?
I’ll be honest and say I haven’t seen this too much lately and in smaller networks it doesn’t usually amount to much of a problem. In larger networks though I’ve seen a lot of performance issues around this scenario.So the easy solution is just don’t place the firewall on the same network segment as any of the desktops/laptops.
Have you ever run into this problem?
Cheers!
In a scenario liked you described I have been making the Cisco 2921 the Gateway and the connecting the ASA to an open port on the 2921 within a new IP range.
Is that how you would do it?
That’s certainly one way to do it Del.
Thanks for the comment!
Hi Michael, great post. For smaller networks I’d go with Del Bullion’s suggestion with the caveat that the amount of traffic destined for both the corporate WAN and the Internet doest oversubscribe the little 2921. On large networks I’d stipulate that the device connecting the hosts to the network is a layer 2 / 3 switch. Configure an SVI on the switch to be the DG for the hosts with a default route pointing at the ASA and the RFC1918 addresses pointed at the 2921 router?
Cheers,
Nick
I used to see this a lot in small companies that just started expanding, but honestly not so much any more. It seems with the cost of L2/L3 switches falling, the dedicated router has been slowly fading away. I am finding more and more the L2/L3 switch is now the default gateway and the firewall/VPN device in it’s own VLAN and the WAN links terminate as Ethernet right on the L2/L3 switch. I am just waiting now till someone drops the firewall/VPN capability in to the switch next.
Hi michael.
I have some avaya 4550t-pwr switches in my office. I am about to implement a voip solution. My question is Do you have a tutorial on how configure it a port when you are going to have data a voice in the same port and both vlans with different DHCP? example vlan data DHCP is 172.16.10.0 and vlan voice 172.16.20.0.
Thank you
Michael; you are one of the few with Nortel experience; I have an odd question…
I have some Grandstream HT701’s unregistered on a stand alone router (no PBX, no Internet), performing IP address dialing. The POTL’s connected to the 701 can receive IP addressed calls, and dial IP addresses as well, using this dialing syntax:
*47192*168*xxx*xxx
The *47 tells the HT701 that this will be an IP addres type call, followed immediately by the other phones IP address. “Stars” are used in place of the decimal on the Grandstream HT701.
I recently aquired a Nortel 1535, and plugged it into the router that connects to the Grandstreams. I was able to “register” the Nortel; and get a dialtone.
Here’s the strange part:
I can dial the Nortels IP from the Grandstreams HT701… and the Nortel will ring and a two way telephone call works fine; the Nortel displays “IPCall” on the screen as the phone rings.
But, I can not figure out how to dial (via IP address) from the Nortel to the Grandstream. I believe it’s a dialing syntax problem; as the Grandstream requires a few tricks in the dialing string, and I assume the Nortel has the same uniqueness. I can’t seem to find instructions on how to dial an IP address from the Nortels. I even tried entering the IP address into the Phonebook contact list; thus trying to dial an IP with a real IP format (using decimals).
Are you aware of any method to dial out -via IP address- on a Nortel?
Tim
Hi there,
DHCP scopes usually accept to send static route entries to the clients. So I will put a last resort to the internet router and a specific one to the ASA firewall.
Another solution will be set only a default and redirection in the internet router for the company behind the firewall.
A bunch more solutions come to my mind. What I strongly recommend is to set always the default in the Internet router and the specific ones separated.
Cheers