 In the two previous posts I covered how to create multiple VLANs, trunk those VLANs between multiple stackable Avaya Ethernet Routing Switches utilizing Multi-Link Trunking and how to create Layer 3 IP interfaces to be used for routing IP packets between those VLANs.
In the two previous posts I covered how to create multiple VLANs, trunk those VLANs between multiple stackable Avaya Ethernet Routing Switches utilizing Multi-Link Trunking and how to create Layer 3 IP interfaces to be used for routing IP packets between those VLANs.
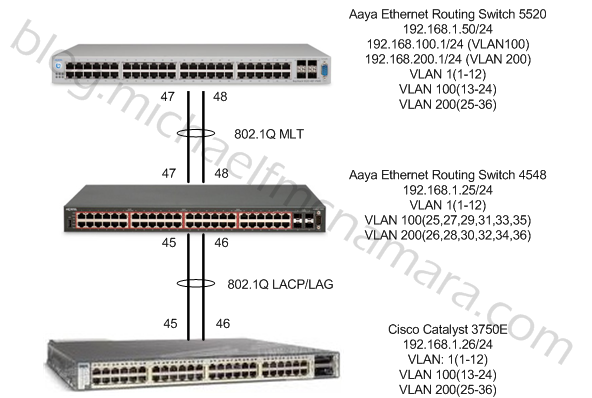
In this post I thought I would expand the network topology of my previous two posts to include a Cisco Catalyst 3750-E. I’ll specifically cover how to trunk (bridge) multiple VLANs between a stackable Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch and the Cisco Catalyst 3750-E and how to configure multiple interfaces in a Link Aggregation Group (LAG) utilizing LACP similar to Avaya’s proprietary MLT feature.
Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4548
enable config t
Let’s start by making ports 45 and 46 trunk ports which will utilize 802.1Q tagging;
vlan ports 45,46 tagging tagAll
Let’s add the VLANs we wish to bridge across the trunk ports;
vlan members add 1 45,46 vlan members add 100 45,46 vlan members add 200 45,46
Now we’ll enable LACP on ports 45 and 46 using the same LACP key which will automatically create the LAG;
interface fastEthernet 45 lacp key 10 lacp mode active lacp timeout-time short lacp aggregation enable exit interface fastEthernet 46 lacp key 10 lacp mode active lacp timeout-time short lacp aggregation enable exit
Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 4548 – Show Commands
4548GT-PWR#show lacp port 45,46 Admin Oper Trunk Partner Port Priority Lacp A/I Timeout Key Key AggrId Id Port Status ---- -------- ------- --- ------- ----- ----- ------ ----- ------- ------ 45 32768 Active A Short 10 12298 8224 32 302 Active 46 32768 Active A Short 10 12298 8224 32 303 Active 4548GT-PWR#show mac-address-table Mac Address Table Aging Time: 300 Number of addresses: 26 MAC Address Vid Source MAC Address Vid Source ----------------- ---- ------- ----------------- ---- ------- 00-02-B3-CB-77-A2 1 Port:19 00-04-61-9E-46-7E 1 Port:21 00-0C-29-64-33-F9 1 Port:19 00-0C-29-A5-CB-54 1 Port:19 00-0F-20-95-38-D5 1 Port:11 00-18-01-EA-F4-45 1 Port: 1 00-1C-11-6B-DC-6B 1 Port: 1 00-1C-11-6D-15-27 1 Port: 1 00-1C-11-6D-15-DC 1 Port: 1 00-1E-7E-7C-2C-00 1 00-1E-7E-7C-2C-40 1 00-1F-0A-CE-BC-01 1 Trunk:1 00-1F-0A-CE-BC-40 1 Trunk:1 00-1F-D0-D0-BE-2D 1 Port:17 00-23-EE-96-AA-21 1 Port: 1 00-24-B5-F6-94-02 1 Trunk:1 00-64-40-CF-4D-AD 1 Trunk:32 00-64-40-CF-4D-AE 1 Trunk:32 00-64-40-CF-4D-C0 1 Trunk:32 00-0A-E4-76-9C-C8 2 Port:44 00-24-DC-DF-0D-08 2 Port:43 00-A0-F8-5E-CE-BC 2 Port:39 00-1F-0A-CE-BC-41 100 Trunk:1 00-24-7F-99-84-70 100 Port:25 00-64-40-CF-4D-AD 100 Trunk:32 00-1E-CA-F3-1D-B4 200 Port:26 00-1F-0A-CE-BC-43 200 Trunk:1 00-64-40-CF-4D-AD 200 Trunk:32 4548GT-PWR#show mlt Id Name Members Bpdu Mode Status Type -- ---------------- ---------------------- ------ -------------- ------- ------ 1 MLT_to_ERS5520 47-48 All Basic Enabled Trunk 2 Trunk #2 NONE All Basic Disabled 3 Trunk #3 NONE All Basic Disabled 4 Trunk #4 NONE All Basic Disabled 5 Trunk #5 NONE All Basic Disabled 6 Trunk #6 NONE All Basic Disabled 7 Trunk #7 NONE All Basic Disabled 8 Trunk #8 NONE All Basic Disabled 9 Trunk #9 NONE All Basic Disabled 10 Trunk #10 NONE All Basic Disabled 11 Trunk #11 NONE All Basic Disabled 12 Trunk #12 NONE All Basic Disabled 13 Trunk #13 NONE All Basic Disabled 14 Trunk #14 NONE All Basic Disabled 15 Trunk #15 NONE All Basic Disabled 16 Trunk #16 NONE All Basic Disabled 17 Trunk #17 NONE All Basic Disabled 18 Trunk #18 NONE All Basic Disabled 19 Trunk #19 NONE All Basic Disabled 20 Trunk #20 NONE All Basic Disabled 21 Trunk #21 NONE All Basic Disabled 22 Trunk #22 NONE All Basic Disabled 23 Trunk #23 NONE All Basic Disabled 24 Trunk #24 NONE All Basic Disabled 25 Trunk #25 NONE All Basic Disabled 26 Trunk #26 NONE All Basic Disabled 27 Trunk #27 NONE All Basic Disabled 28 Trunk #28 NONE All Basic Disabled 29 Trunk #29 NONE All Basic Disabled 30 Trunk #30 NONE All Basic Disabled 31 Trunk #31 NONE All Basic Disabled 32 Trunk #32 45-46 Single DynLag/Basic Enabled Trunk
You might be looking at the output above and asking yourself what’s “Trunk 32”? Let me provide some quick background. You can have a total of 32 MLT/LAG trunks on a stackable Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch. When you create LACP trunks the switch automatically creates a LAG in the MLT table dynamically from the bottom up. While in the previous post I created “Trunk 1” by trunking ports 47 and 48 together (see above), in this post I’ve created an LACP trunk on ports 45 and 46 which will be reported it the switch as “Trunk 32”. You can also see it in the MAC/FDB table above.
Cisco Catalyst 3750-E
enable config t
Let’s give the switch an IP address in VLAN 1 for management;
vlan 1 ip address 192.168.1.25 255.255.255.0 no shut exit
Let’s create VLAN 100 and VLAN 200 on the switch;
vlan 100 name "192-168-100-0/24" exit vlan 200 name "192-168-200-0/24" exit
Let’s add the appropriate edge ports to each VLAN;
interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/1-12 switchport access vlan 1 exit interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/13-24 switchport access vlan 100 exit interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/25-36 switchport access vlan 200 exit
Let’s configure ports 45 and 46 as trunk ports and bond them together in channel-group utilizing LACP;
interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/45 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk channel-protocol lacp channel-group 1 mode active interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/46 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk channel-protocol lacp channel-group 1 mode active
Cisco Catalyst 3750-E – Show Commands
SW-3750-E#show lacp neighbor
Flags: S - Device is requesting Slow LACPDUs
F - Device is requesting Fast LACPDUs
A - Device is in Active mode P - Device is in Passive mode
Channel group 1 neighbors
Partner's information:
LACP port Admin Oper Port Port
Port Flags Priority Dev ID Age key Key Number State
Gi1/0/45 FA 32768 001e.7e7c.2c00 16s 0x0 0x300A 0x2D 0x3F
Gi1/0/46 FA 32768 001e.7e7c.2c00 27s 0x0 0x300A 0x2E 0x3F
Switch#show mac address-table
Mac Address Table
-------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports
---- ----------- -------- -----
All 0100.0ccc.cccc STATIC CPU
All 0100.0ccc.cccd STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0000 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0001 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0002 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0003 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0004 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0005 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0006 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0007 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0008 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0009 STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.000a STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.000b STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.000c STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.000d STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.000e STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.000f STATIC CPU
All 0180.c200.0010 STATIC CPU
All ffff.ffff.ffff STATIC CPU
1 0004.619e.467e DYNAMIC Po1
1 000c.2964.33f9 DYNAMIC Po1
1 000c.29a5.cb54 DYNAMIC Po1
1 000f.2095.38d5 DYNAMIC Po1
1 0018.01ea.f445 DYNAMIC Po1
1 001c.116b.dc6b DYNAMIC Po1
1 001c.116d.1527 DYNAMIC Po1
1 001c.116d.15dc DYNAMIC Po1
1 001e.7e7c.2c01 DYNAMIC Po1
1 001e.7e7c.2c2d DYNAMIC Po1
1 001e.7e7c.2c2e DYNAMIC Po1
1 001f.d0d0.be2d DYNAMIC Po1
1 0023.ee96.aa21 DYNAMIC Po1
1 00a0.f85e.cebd DYNAMIC Po1
100 0024.7f99.84e9 DYNAMIC Po1
200 0008.02e4.890a DYNAMIC Gi1/0/25
200 001e.caf3.1db4 DYNAMIC Po1
Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 37
You might be asking why didn’t I assign the VLANs to the trunk ports on the Cisco Catalyst 3750-E… well with Cisco switches a trunk port is by default a member of all the VLANs that exist on the switch. So you don’t need to specifically add a VLAN to a trunk port, however, you can override the default behavior by telling the switch to only carry specific VLANs on a specific trunk port – this is called VLAN pruning.
Please feel free to point out any inconsistencies or errors I might have made.
Cheers!
Also important is that Cisco implements STP in a per-VLAN fashion rather than CST. If the Avaya acts the same as it’s Nortel predecessors it will take the link down if there is a loop in VLAN 1 regardless if any other VLANs are loop-free. This makes life difficult when you want some VLANs to act as point-to-point links for routing purposes and others for more expansive topologies that will likely have loops.
Hi JT,
The default behavior/configuration of the Nortel/Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch has legacy Spanning Tree enabled where you have a single CIST, as you referred to above. You can enable RSTP or MSTP with the following command;
Although JT has a great point in that you certainly need to consider Spanning Tree in your design.
Thanks for the comment!
Hi Michael,
Great information on your site. This is first time I visited your site and appreciate knowledge sharing. I have difficulty to get to the end of the page, so I took liberty to post here.
I have confusion here after reading this post (no prior Nortel experience but sufficient Cisco), the Cisco switch has management IP in VLAN1 and this is native / untagged by default on the trunk / uplink to the Nortel 4500 switch, which has all vlans tagged.
How does the untagged management frames go thru them? When you say tagall, does this imply that default vlan 1 is always untagged (unless default vlan id is changed and then that becomes untagged on 802.1q uplinks in Nortel) or do we really need something like vlan 45-46 tagging untagpvidonly?
I found your site while doing a Google search, wherein I am trying to set up a ring on 4 sites in campus over fiber / radio using 4500 switches each thus connecting on east and west side to the other site /4500. Actually all sites sites are connected via 3 intervening fiber circuits and there was a fiber issues a month ago, so we thought to put a radio between site 1 and site 4 to close the loop (radio is transparent IP wireless bridge and passes vlan tags and needs its management vlan (which is vlan 1 as was set up by someone) to be untagged.
So when we tried to connect the radio bridge, assuming, the STP will kick in and block one port somewhere on the uplinks and all will be good, but it does not work as it results into a loop.
Regular STP is enabled on all 4500 switches, and I have set up PVID of 1 on these two uplinks going to the fiber / radio loop and then also tried used tagging untagpvidonly on these, but then reverted back to tagging tagall.
I will also like to assign a higher port cost to the port that goes to the Radio at say site 4, so that STP will normally block that port and keep other 1 Gig fiber links forwarding. But I cannot find how do I assign STP port cost of say 40 (default STP legacy 1 Gig port cost is 4) to the corresponding uplink port on 4500 switch. There is a config line with port cost 1 priority 80, not sure what this port cost 1 mean here, on all switches, even with legacy dot1d costing, it should be 4).
So something like that I have in the main 4500 switches at each location. Any help will be greatly appreciated.
vlan 1 name “Ring”
vlan 2 users
vlan 3 servers
vlan port 45-46 pvid 1
vlan port 45-46 tagging tagall filter-untagged-frame disable filter-unregistered-frames enable priority 0
(this is where I tried replacing tagall with untagpvidonly) and I assume tagall in combination with pvid of 1 on these ports makes the uplinks to have native vlan 1 for untagged frames).
vlan mgmt 3
spanning-tree cost-calc-mode dot1d
spanning-tree port-mode normal
spanning-tree stp 1 priority 8000
spanning-tree stp 1 hello-time 2
spanning-tree stp 1 forward-time 15 max-age 20
spanning-tree stp 1 tagged-bpdu disable tagged-bpdu-vid 4001
spanning-tree stp 1 multicast-address 01:80:c2:00:00:00
spanning-tree stp 1 add-vlan 1
spanning-tree stp 1 add-vlan 2
spanning-tree stp 1 add-vlan 3
spanning-tree port 45-46 learning normal
spanning-tree port 45-46 cost 1 priority 80
spanning-tree bpdu-filtering port 45-46 timeout 120
no spanning-tree bpdu-filtering port 45-46 enable
Thanks
Hi dpsguard,
Unfortunately there’s an issue with the theme I’m using on my blog that is “hiding” replies on some of the more commented posts. I really need to address that problem since I value the comments and feedback that everyone provides.
Your post is exceptionally long and detailed, so don’t think ill of me for not replying in such length. I would encourage you to post over in the discussion forums where myself and others will try and bring you up to speed.
You might also want to check out this post;
http://blog.michaelfmcnamara.com/2012/02/untagall-vs-tagall-on-avaya-ethernet-routing-switches/
In short with a port set to UnTagAll, there should only be a single VLAN assigned to that port and all frames are untagged. With a port set to UnTagPvidOnly, there can be multiple VLANs assigned with the “Default PVID” being untagged the remaining VLANs being tagged – this is equivalent to Cisco trunk behavior.
Unfortunately I don’t have the time right now to reply with any more detail.
Cheers!
Hi Michael,
Great blog! Some really useful tips, good of you to give your time to it.
Is it possible to split a Cisco switch between an IST pair of say ERS5530s? Would the ERSs need a LAG on each rather than SMLT/MLT?
Thanks,
Rob
Hi Rob,
I believe the ERS 5000 series supports utilizing 802.3ad (LACP) over SMLT.. I know the ERS 8600 can I’m just not 100% sure about the lower models.
Cheers!
HI Can u pls tell me I have one Norte 4558GT switch and one cisco 2960.
I want to connect Cisco 2960 switch with Nortel 4558GT. pls
tell me what config should i apply on both end of switch for
properly communication in between both switch.
Hi Parvesh,
You can use the same commands above that I provided for ERS 5520 for the ERS 4500.
Good Luck!
Love your site so much!
I have seen an issue with this type of configuration. Here’s the scenario:
Cisco switchconfigured with a 2 member EtherChannel to a Nortel Switch
Members/PortChannel is an access port (VLAN 1)
Default PVST configuration is used
EtherChannel mode set to on
Nortel is configured with a 2 member MLT to the Cisco Switch
Default Nortel STG is used
In this configuration, the Cisco EtherChannel will be ErrDisabled as a spanning tree loop is detected. I just ran into this situation. Here’s my question:
I would rather not disable spanning tree, and notice that there is an option in the DM called NtStgEnable. It is described as turning on/off nortel STG mode. It is using Nortel mode by default.
Will disabling this option correct this behavior? I can’t find any conclusive documentation on it..
Hi Scott,
You should review this article; http://blog.michaelfmcnamara.com/2011/06/avayas-multilink-trunk-and-spanning-tree-protocol/
You need to configure the Avaya/Nortel switch for MSTP (the default is STP) and then enable “mlt 1 bpdu all-ports” on the specific MLT.
Good Luck!
Hi Michael,
Great post. I had an issue in a similar setup posted here, and customer created a loop between cisco and avaya switch through avaya phone connected to avaya 4826 switch. Cisco 4507 switch is on etherchannel, with pvst. Avaya never trigger bpdu filter in such scenario and cisco etherchannel ports go down, can you help with expert opinion.thanks.
I would verify that Spanning Tree (FastStart) was enabled along with BPDU filtering. I’ve seen it done dozens of times here and it always kicks off the port. There was a very early release of software/firmware for the i2002/i2004 IP phones which had an issue when both ports were connected to the switch, I believe they were filtering the BPDU frames which allowed the loop.
Ultimately you’d need to simulate in a testlab to see the real story.
Cheers!
I haven’t done much with VLAN’ing, but where in this article did it tell us how to enable VLAN tagging on a Cisco 3750 stackwise switch? Thanks!
Mark
Hi Mark,
You only need to enable dot1q on the physical interface to enable VLAN tagging;
Cheers!
Thanks for the quick reply! If you have a sec, maybe you can help me with a problem. Here is the explanation:
I am trying to setup a seperate vlan to go to a seperate WAP in my network, so I can provide guest internet access without my production network being visible. I’ve set it up, but it is not working. I created a sub-interface for the new vlan (VLAN 12) on my ASA5510 firewall. The new VLAN is 172.72.72.0/28, for example. I gave it an ip on that sub-interface of 172.72.72.1. Then, I connected the WAP and configured it to be on that VLAN and subnet. I found out the WAP isn’t DHCP (server) capable, so I set the ASA to act as the DHCP server for that VLAN. I connected a laptop wirelessly and it received an ip address from my normal inside DHCP server…??? How did it do that??? Also, I could get out to the internet and see the rest of my network. So, then I set the port on the switch that the WAP is connected to, to be on that VLAN only and now, my laptop won’t get an ip at all. So, just to see if the rest of the configuration is good, I statically assigned an ip address for that subnet on my laptop and I could see the WAP, but not the firewall. I tried pinging the sub-interface on the firewall and couldn’t. Also, I can ping the WAP, but I can’t actually access it via the web interface. But, if I leave that 172.72.72.x static address on the laptop and connect to my production wireless, I can get to the web interface of the WAP, but no where else. I’m not sure where I went wrong here. Any thoughts?
Thanks!!!
Mark
Hi Mark,
Your question isn’t really on topic but I’m still happy to help. Post your problem over on the discussion forums and I’ll be sure to respond (along with quite a few other people I suspect).
Cheers!
I posted that in the Cisco Routers and Switches forum. Thanks again for you help!
Mark
You’re welcome Mark!
Hello Michael,
This configuration works with Server too?
Regards,
Hi Cesar,
Assuming the server supports LACP it should certainly work.
Cheers!
Hi Michael,
I have tried configuring LACP between Avaya 4548GT & Cisco 2960 as per the instructions in your blog http://blog.michaelfmcnamara.com/2011/01/802-1q-vlan-tagging-on-a-cisco-catalyst-3750-e/, but one of my etherchannel port on cisco switch always remains in suspended mode. could you please help me in sorting out the same.
Regards
Rajesh Bisht
Hi Rajesh,
You need to determine why the port is being suspended. Are you running Spanning Tree? What’s in the log files?
Good Luck!
Hi Michael,
there is nothing on the log which suggest anything about this problem. I t just says that the port is up. I think Spannning-tree is by default up on Cisco switches & I have not disabled it manually.
On the Avaya switch it is enabled on the port where this trunk cable is connected.
Regards
Rajesh
HI, very useful post . But if I need to aggregate links from 3 ERS 4550 to 1 HP switch :
1 Do i need to setup DMLT and setup LACP ? I tried to setup MLT but it’s don’t want to work with LACP on ERS4550 ..
or LACP will be enough for that 3to1 setup ?
Hi Bekzod,
Any comments made to this blog by first time posters are held for moderation. I deleted your second post.
You didn’t mention if the 3 ERS 4550s were in a stack configuration. You could certainly follow the steps outlined above to add additional ports to the trunk group. Assuming the HP switch supports LACP you should have what you need concerning the Avaya switch below.
Good Luck!
Thank you . So if I have a stack of ERS 4550 and 1 GB link from each of the 3 to 1 HP switch (support LACP) then I don’t need to setup MLT and LACP will be enough . Correct ?
I like how you help and because of we are working mostly with Avaya I will often bother you ;) .
Best Regards .
When you setup LACP it will automagically create an MLT.
Cheers!
Hi Michael,
Thanks for swift response. When we configure mstp on both ends( even without creating instances on it), now it kicks off and either of the switches shut the port. However things does not work when phone is off, loop is created, and then the phone is booted. Seems during booting of phone bpdu are not passing through as I can see only LLDP packets in traffic. Phone is avaya 1000 series. What’s your view on this?
Hi Michael,
Just wanted to point out that I noticed a typing error on the interface range gigabitEhernet 1/0/24-36 line shouldn’t it read interface range gigabitEhernet 1/0/25-36 since the port1/0/24 was already assigned in the line above.
interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/1-12
switchport access vlan 1
exit
interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/13-24
switchport access vlan 100
exit
interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/24-36
switchport access vlan 200
exit
Thanks Dan. I’ll update the post.